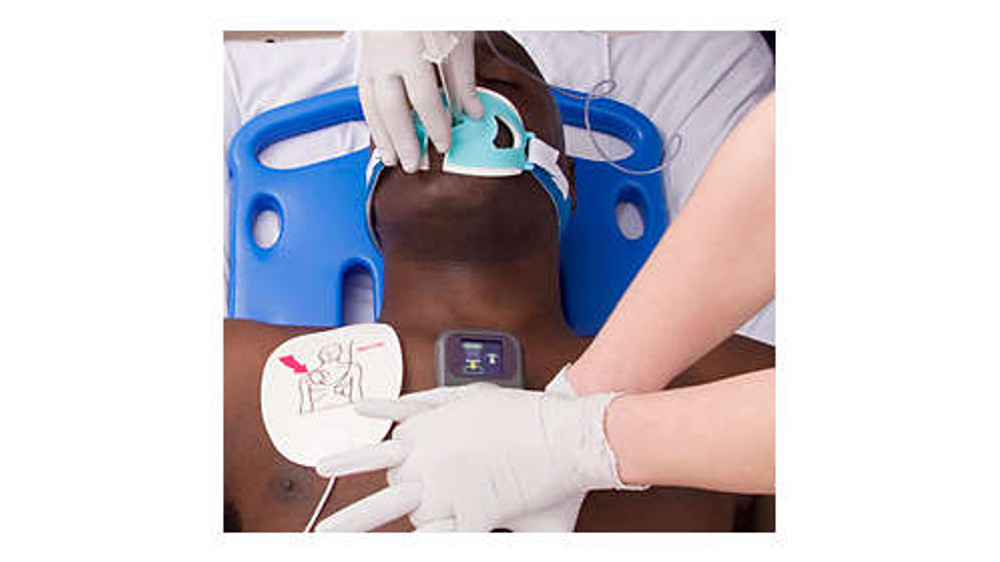
Q-CPR is the most clinically proven CPR measurement and CPR feedback tool, and next-Generation Q-CPR is available as a fully integrated option with the HeartStart MRx Monitor/Defibrillator and offers several vital advances, based on the latest research, and input from current Q-CPR users:
- The award-winning digital Q-CPR meter enables you to rapidly adjust performance with dynamic, real-time feedback for each compression, displayed directly at patient chest level
- In your hands, the Q-CPR meter helps ensure that every compression meets depth, rate, and complete release targets to help improve the patients chance of survival and increase the opportunity for a complete neurological recovery
- Q-CPR features enhanced visual feedback and voice prompts that are configurable to OFF for those times when silence is best
Only Q-CPR provides hyperventilation protection
Hyperventilation is relatively common and harmful during CPR, and only Q-CPR provides hyperventilation protection. Science shows that hyperventilation decreases coronary perfusion and research indicates that excessive ventilations are common. Competitors are unable to provide ventilation measurement or feedback of any kind. Without measuring ventilation, how do you know what the ventilation rate is during resuscitation?
Reinforce effective CPR technique
Data generated by Q-CPR and presented by Event Review Pro provide the objective evidence required to reinforce effective techniques and motivate change where needed, enabling system-wide QA/QI and supporting continuous CPR training.
In a recent study, the HeartStart MRx with Q-CPR was used to record resuscitation performance during actual cardiac arrest events. When medical professionals then participated in weekly debriefing sessions in addition to real-time feedback from Q-CPR, improvements were shown in CPR performance, and correlated with an increased return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
Q-CPR is a trademark of Laerdal Medical.
1. Ko PC, Chen WJ, Lin CH, et al. Evaluating the quality of prehospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation by reviewing automated external defibrillator records and survival for out-of-hospital witnessed arrests. Resuscitation. 2005;64:163-169.
2. Edelson DP, Litzinger B, Arora V, et al. Improving in-hospital cardiac arrest process and outcomes with performance debriefing. Arch Intern Med. 2008; 168(10):1063-1069.